
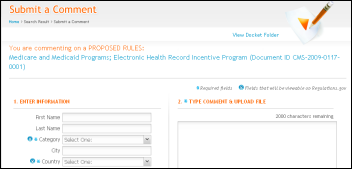
From Nurse Carol: “Re: meaningful use. Will you provide links and document numbers for commenting on the proposed rules?” I e-mailed ONCHIT just to make sure I understood the process and they kindly verified: the 60-day comment period starts with the date the rules are published in the Federal Register, which is scheduled for next Wednesday, 1/13. Comments can be left on regulations.gov. I’ll run the exact link once it’s available.
From Nosy me: “Re: GE. GE has put their Centricity EMR implementation on hold at UMDNJ School of Osteopathic Medicine due to lack of payment. UMDNJ, the health university of New Jersey, contends that they have gotten nothing for their investment so far except extended timelines and escalating bills.” Unverified.
From The PACS Designer: “Re: Thoma Bravo LLC. PACS vendor AMICAS has decided to accept an offer from Thoma Bravo LLC to buy their shares at $5.35/share. TPD is very familiar with AMICAS and their acquisition of Emageon. While the AMICAS PACS is a great product, the Emageon PACS is just the opposite and the reason AMICAS may want to go private is to keep their shareholders from finding how bad things really are with the Emageon product line. Having Thoma Bravo LLC is just what the patient (AMICAS) needs to get better!”

From IKnowPlenty: “Re: things that make you go ‘hmmm’. The keynote address for AHA’s annual leadership meeting is disgraced climatologist Al Gore. I fail to understand what he has to do with healthcare or hospitals, other than wanting to sell them carbon credits.” He finally got his big house LEED certified once word got out on the Internet he invented that his electricity usage was more than a dozen times the average. He’s about as relevant as the other speakers, though: Freakonomics guy Steven Levitt, former White House secretary and Vanity Fair editor Dee Dee Myers, and film maker Ken Burns. You know it’s a stretch when the guy with the most relevant healthcare credentials is talking head Sanjay Gupta. These folks don’t speak free, so your hospitals (meaning patients and taxpayers) are footing their bill. According to tax records, AHA took in $120 million last year, of which $22 million was pure profit (in a non-profit way). Three of its executives made more than $1 million, the CEO made $2 million, and all are appalled that anyone would suggest that healthcare reform is needed.
From FinSoft: “Re: QuadraMed. Steven Russell gets 86’d as collateral damage from the Dunn hiring.” The 8K also gives Tom Dunn’s hiring details.
From Nasty Parts: “Re: Sage. I hear they will announce a new president shortly and Lindy Benton will stay on as SVP of sales.” Unverified, although Nasty Parts has a pretty good track record.
From CongestiveITFailure: “Re: CCIM. Community Care Information Management, another Ontario Ministry of Health and Long Term Care eHealth agency, is currently being run by the partners from Blue Pebble, a consulting firm. There is a serious conflict of interest, as Blue Pebble hires their own eHealth subcontractor consultants and places them (on a contract basis) within CCIM. They take a percentage of their subcontractors’ daily rate and pay them via a third-party vendor so as to skirt current provincial salary disclosure rules. The partners from Blue Pebble consulting were put together by the current Ontario MOHLTC Associate Deputy Minister John McKinlay. Another scandal is imminent with such a conflict of interest.” Unverified, but I found this October article that says the same thing. Three of the project’s senior managers set up Blue Pebble and then got 30% of the project’s consulting business. CBC says Blue Pebble also did work for the disgraced eHealth Ontario and its predecessor, Smart Systems for Health Agency. An anonymous informant said Blue Pebble was using the government’s people and technology and charging them for it.
From MalaysiaHITFan: “Re: HIT vendors. Surprised no announcement out of HIT vendors on what are presumably sizeable contracts. Focus on openness must be why Epic missed the cut.” I saw the article, but couldn’t decide whether I was interested in it. Malaysia awards contracts to Microsoft, Eclipsys, Cerner, and IBA Health for new systems, although the date of those contracts isn’t mentioned, so I’m thinking its old news. Still, the projects are interesting: teleconsultations, personalized education, CME, smart cards, and a Lifetime Health Plan for every citizen (which the article candidly says “became the biggest failure of the Ministry” when the business model turned out to be shaky and the managing company went bust). Now they’re doing an HIE instead.
Cardinal Health announces a bar code-powered inventory and ordering system called Connect System (catchy name) for laboratories.
Wait … what’s that sound? Someone crying out for help? Why, it’s my HISsies nominations, pining for some Web-based intimacy with all those knowledgeable HIStalk readers who would be the first people I would ask to name the Industry Figure of the Year, the Best and Worst Vendors, the CIO of the Year, and of course the happy winner of The Pie. The upcoming voting won’t be all that interesting if the only nominations I get are from vendors nominating themselves for the good awards and their most hated competitor for the bad ones. I’ll close the nominations out this weekend, so vote now or forever hold your peace.

Twin County Regional Hospital (VA) expands its McKesson Paragon implementation to include Practice Partner. It’s in Galax, a town I like although I’ve been only a couple of times (the Rex Theater for live bluegrass, Aunt Bea’s for barbeque, and a bounty of fiddle players).
The College of American Pathologists releases its updated XML version of the CAP Cancer Checklists, used for cancer description and reporting.

Many thanks to Wellsoft, new on board as a Platinum Sponsor of HIStalk. What you should know about the company: (a) it offers a highly awarded emergency department information system; (b) Version 11 has some cutting edge new features (anatomical diagrams, clinical decision support, medication reconciliation, and a patient entry kiosk), and (c) the Wellsoft EDIS has some powerful technology behind it, such as Oracle, interfaces to all hospital information systems, remote updating, guaranteed 15-minute support response time, and custom reporting. Get on their mailing list here and check out the video. They will be in Booth 7005 at HIMSS, FYI, which reminds me that a couple of years ago at HIMSS, I went to some super-geeky, small-room session on clinical decision support architecture or something like that and I noticed a casually dressed, deeply immersed guy sitting a couple of seats over. I checked his badge and it was John Santmann, MD, founder of Wellsoft. I don’t think I’ve ever seen a CEO in a real HIMSS session and a hardcore one at that, so I admired him immediately. End of pointless anecdote.
Hocking Valley Community Hospital (OH) will implement Keane Optimum iMed and migrate to Optimum Patcom.
I’m all for free speech, but the same people posting the same comments about EMR safety and FDA regulation under multiple phony names (yes, I can tell) is wearing a bit thin. I sometimes agree with the argument, but I don’t need it jammed down my throat several times a day. Would I be wrong to delete those comments?
Listening: a recommendation from Tom in Verona, WI (gee, wonder where he works?): Nothington, polished and pop-tinged punk that immediately motivated me to attempt a frowning-faced, intense desk drum solo that nearly slung the watch off my arm. An excellent choice. I was going to listen to part of just one song to be nice to Tom, but I keep playing them over and over.
Vanderbilt opens BioVU for internal research projects with IRB approval. It’s a DNA data bank with 75,000 samples linked to the de-identified EMR records of their owners. One of the first studies will look for a relationship between DNA and drug response.
I got some info on the contract between Universal Health Services and Cerner. It’s a pretty big rollout: ED, clin doc, orders, CDR, meds, biomedical device integration, LIS, pharmacy, and OR. Not ADT or accounting, which are notoriously weak links of Cerner (heard much about ProFit lately? Exactly.)

Practice management vendor AdvancedMD acquires EHR vendor PracticeOne, hoping to roll the products together into a SaaS solution.
This might make a good remote hosted EMR commercial: thieves break into a medical practice and steal its Fujitsu Lifebooks, but as the CEO tells the reporter, “None of the electronic medical records reside on the computers or on our property” since they use a hosted service.

Capital Regional Medical Center (FL) publishes its ED wait time to the iPhone via iTriage.
Several former executives of iSoft, including the former chairman and CEO, face criminal charges in Britain for making false and misleading statements.
AT&T will launch five Android-powered mobile phones in the next few months, one made by Dell and another rumored to be a version of Google’s just-announced Nexus One.
At the International Consumer Electronics Show, Cisco demonstrates a home version of its TelePresence videoconferencing system, showing how it could be linked to medical devices to pass voice, video, and data from patient to physician. At the same show, Skype announced that its application is now capable of making high definition video calls and will be incorporated into HDTVs (as a newfound Skype Video user not even using HD, video calls via Skype are still one of the coolest things ever, just like being in the room with the person on the other end of your free call).
Two Regenstrief informatics fellows win AMIA student awards, one for a graphical tool to examine drug interactions, the other for a system that proposes drug and lab suggestions based on physician ordering habits. I’m thinking I should cover more of this research-based informatics stuff since it interests me and it’s innovative.
eClinicalWorks will offer patient education from Krames, including 1,300 aftercare instructions in several languages that are suggested to physicians based on EMR information as well as for direct patient access through eCW’s patient portal.
Odd lawsuit: an MRI clinic’s car injury claim is fully paid by its insurance company, receiving the state-allowed maximum $10,000 in PIP benefits. Their attorney sues the insurer for $2.59. For once, an insurance company gets to accuse someone else of being a scumbag. “Who has the greater motivation to sue in this case, the MRI clinic that’s seeking $2.59 or an attorney who charges about $375 an hour for his services?”
E-mail me.
HERtalk by Inga
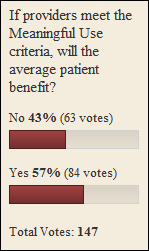
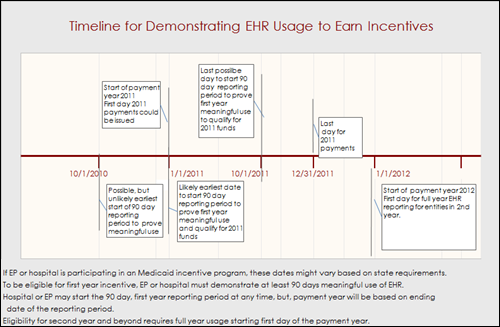
From Father Time: “Re: meaningful use timeline. It is my belief that the MU clock will start ticking 10/1/2010 as that is the start of the government’s 2011 fiscal year. I am certainly no authority on the subject, but it would seem the government would use their year vs. calendar or any other for the time period used to verify meaningful use of hospitals and providers. If you consider that time period and use the HMS/CMS 90-day model, a hospital would have to begin to prove meaningful use BEFORE July 1, 2011. In hospital years, that is REALLY soon!” I agree with Father Time that the MU clock could start as early a 10/1/2010 for hospitals (in fact my graphic indicated that). HIMSS also said 10/1/2010 in their webinar this week. However, the committee’s “recommendation” is that the Secretary choose the calendar year (starting 1/1/2011) for meeting the definition, which would give both hospitals and vendors more time to ramp up.
From CPOE Guy: “Re: EMR and girl talk. Maybe I don’t understand girl talk, but those of us providers using Epic (Kaiser for example) are doing at least 99% order entry; in my case it’s 100%. The only exceptions in our organization is for super emergency verbal orders during codes where the doc can’t get to a computer, and even there it is frowned upon. Our prescribing is 100% electronic for normal Kaiser patient prescriptions not requiring written (the former ‘triplicates’ such as morphine, Ritalin). I write handwritten prescriptions only for non-Kaiser patients who wish to fill their meds elsewhere and even then, I enter these electronically into the EMR to keep our record complete.”
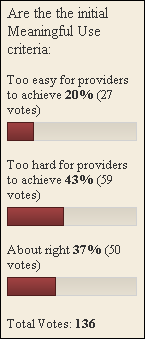
From Outta Touch: “Re: Latest meaningful use guidelines. In the last few days, I’ve asked a few doctor acquaintances about their impressions on the latest proposed meaningful use definitions and certification guidelines. Most have simply given me a blank stare, asking what I was talking about. Am I running with the wrong crowd or is the average doctor just not interested?” My guess is both. Who wants to hang out with doctors that can’t talk techie? Give me a Dr. Alexander or Dr. Diamond any day. And, I suspect that most doctors are more concerned with practicing medicine and getting paid then they are with dealing with the minutiae. Most practices have at least one doctor or an administrator who is more interested in following the specifics. Plenty of doctors are happy to defer to the “experts” until they are handed a tablet and told to enter a prescription.
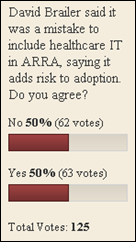
From Jabez William Clay: “Re: draft rules on the EHR incentive plan. Have you guys seen this?” The CSC study that indicates US hospitals are only halfway ready to qualifying ARRA payments. In fact, only two-third of hospitals have identified gaps in their current systems. A quarter of the 58 hospitals think they meet at least 70% of the readiness criteria.
From Felice Fontanta” “Re: ARRA questions. Thanks for your analysis! Very helpful. A few questions I haven’t seen answers to yet: How and when are the funds going to be disbursed? Say you demonstrate MU in the 1/1/2011 – 3/31/2011 time period, when and how will you be paid your $18k? And, In terms of qualifying docs, is the Medicare program restricted to Medicare providers? So a pediatrician would not be eligible for any funds unless they have a significant Medicaid panel?” The legislation says that incentive payments be disbursed in a single consolidated payment or in periodic installments, as the Secretary may specify. However, the recommendation is for a single lump payment “as soon as we ascertain” meaningful use for the applicable reporting period. Regarding participation in the Medicare incentive program, it is restricted to Medicare providers. Pediatricians can participate in the Medicaid program if at least 20% of their patient volume is Medicaid.
Mr. H and I have had multiple questions posed to us regarding the latest certification and meaningful use recommendations. We don’t claim to be experts, but we are happy to try to get clarification on certain points if we can. Here are a few FAQs that we have gathered from readers, this week’s HIMSS webinar, and the CMS website:
Q: To count as CPOE, must the provider personally (hands on keyboard) enter the order, or may physical entry of the order, under the provider’s direction, be done by other staff?
A: The reg states “directly”.
Q: Our pathologists are employed by a clinic and physically work in a clinic. Do they qualify as eligible Medicare outpatient providers?
A: Depends on whether the clinic or the hospital provides the facilities or the equipment.
Q: Is an eligible hospital is only an acute care facility or does it include other types of facilities, such as rehabilitation facilities?
A: CMS uses the "CCN" – the CMS certification number assigned to each hospital – to assess whether or not a hospital is eligible.
Q: If a hospital ER is using CPOE for all orders, does it qualify for the 10% of CPOE for a hospital?
A: The ER is counted as outpatient, so no, it will not fulfill the 10% CPOE requirement for an inpatient facility. (HIMSS waffled a bit on this during their webinar but finally came to this conclusion.)
Q: On the hospital side, must the physician enter the CPOE order directly? Or may they have their MA do the entry under their authority?
A: The reg states "directly".
Q: If only 10% of the hospital’s staff is using the certified system, and the rest are still paper-based, would this satisfy the CPOE requirement?
A: The requirement is that 10% of all orders be entered by CPOE.
Q: Do State Mental Health Hospitals qualify for incentive payment? What about long term care providers such as nursing homes?
A: No. The following types of institutional providers are eligible for incentive payments under Medicare and/or Medicaid provided they meet the applicable criteria. Under Medicare, institutional providers eligible for the EHR incentive payments include “hospitals" as defined under section 1886(d) of the Social Security Act and critical access hospitals. Under Medicaid, these institutional providers are acute care hospitals and children’s hospitals.
Q: If you are a provider or hospital and not a meaningful EHR user, when do the penalties kick in?
A: Starting in calendar year 2015 for physicians and FY2015 for hospitals. At that time, CMS will begin to reduce Medicare Market Basket adjustments. There are no payment adjustments associated with the Medicaid provisions.
Q: How will the public know who has received incentive payments under the Recovery Act? 
A: CMS will post the names of those receiving Medicare incentives online. The list will include the elements identified in the Recovery Act: name, business addresses, and business phone number of all Medicare eligible professionals and hospitals who received incentive payments under the Recovery Act. There is no such requirement for CMS to publish the names of those receiving Medicaid incentive payments,though States may opt do so.
That last fun fact was Mr. H’s favorite, by the way. Surely it will be a boon to telemarketers who will have all the information required to pounce on the nouveau riche doctors.
SCI Solutions launches Schedule Maximizer (v32) which includes e-mail appointment reminders, expanded portal functionality, and several new revenue cycle reports.

An Arkansas doctor is indicted for planting a bomb that critically injured the chairman of the Arkansas Medical Board last February. Dr. Randeep Singh Mann, who had been previously penalized by the Arkansas Medical Board for overprescribing medication, was charged with planting a car bomb that left the board chairman with blindness on one eye, damaged hearing, and several broken bones. Mann was already facing federal weapons charges for possessing unregistered machine guns and explosives that are permitted only for military use.

Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center (NC) selects QuadraMed’s Enterprise Scheduling for scheduling hospital ancillary procedures.
Allscripts strikes a deal with CVS Caremark to migrate thousands of users from the proprietary CVS iScribe e-prescribing tool to Allscripts e-prescribing.
Surgical Information Systems picks up an endorsement from the American Hospital Association for its surgery scheduling system.
Our favorite pink pants-wearing friends at Voalte say their Voalte One iPhone application is now generally available, following a successful pilot program at Sarasota Memorial Hospital (FL).
CHIME raises some concerns about the newly released meaningful use regulations, particularly with the short timeline for hospitals to implement EHRs. They believe that the 2014 deadline for hospitals and EPs to meet Stage 3 criteria is too soon. CHIME also says the extensive reporting requirements will be burdensome for hospitals. And, CHIME points out that since hospital-based physicians aren’t eligible to receive stimulus funds, it may create a disincentive for health systems to invest in ambulatory EMRs. To that last point, I don’t quite agree, since hospitals will need the physicians to have EMRs to meet interoperability requirements.

E-mail Inga.






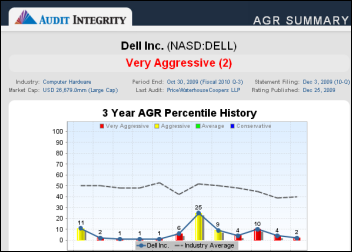
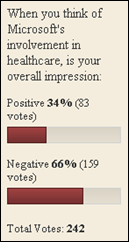




































































There was a time when my company went through multiple rebrands. These were relatively minor shifts, but completely unnecessary. It…