HIStalk Interviews Gadi Lachman, CEO, TriNetX
Gadi Lachman, LLB, MBA is president and CEO of TriNetX of Cambridge, MA.

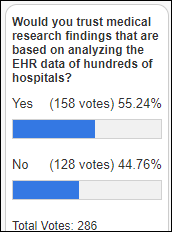
What was your reaction when you heard that prominent medical journals retracted two COVID-19 research articles due to concerns about the quality of the underlying aggregated EHR data that researchers analyzed?
It’s easier for me to talk about what we do and how we do it as opposed to talking about other companies. I’ve never heard of Surgisphere, the organization whose data was used.
EHR data is super valuable. In the world of clinical research, you want to use all the tools available to develop therapies, to develop cures, and to save human lives on a massive scale. That goes without saying. There is a powerful do-good in this industry of utilizing data for drug development, for therapy development, to fight disease, and to find cures.
Then, what is data? There are many different categories of data. Claims data, EHR data, data collected in the lab in the process of a clinical trial, patient-reported outcomes, and things like that. EHR data is forever being used in the clinical research realm. Every data type has its pros and cons, and every data type has a lot of value in helping those who develop new cures and new therapies.
I would almost say when you’re developing a new cure or you’re trying to understand a disease, you cannot do that without looking at EHR data, because that tells you what happens in the inpatient and outpatient settings. What happens with those patients? What therapies, what diagnoses, what medications, what do they report as going on with them, and what is the medical community doing to them? Then you follow to see the outcomes of those interventions.
EHR data is fundamentally basic for clinical research and has been widely and popularly used in that space. The question becomes, how can you ensure the quality? How do you know, as a researcher, what data you are looking at and what processes have been put into place and how much capital and human labor has been deployed to ensure the quality of the data?
TriNetX is a global network. We are in 26 countries. We take data for more than 150 healthcare organizations, including the likes of Johns Hopkins, Boston Children’s Hospital, MUSC, University of Iowa, and others. We work with many, many pharmaceutical companies, such as Sanofi, Novartis, AstraZeneca. We interact as a trusted advisor with those healthcare institutions. We are making sure that this EHR data can be used for clinical research. We look at it, we test it, and we compare it to other big data that we have to make sure it’s consistent. We look at how people are coding and inputting the data and report back any inconsistencies. We compare structured data to unstructured NLP data and see if there are discrepancies.
We have deployed $150 million of capital to accomplish that. We have people all over the world. We have data scientists who make sure that the data is clean and consistent. That data is getting a lot of love and attention. It gets to a level of quality where a researcher can say, I trust it. It makes sense to me. I’m going to research on it. I’m going to publish on it. It takes a lot to get to a level of quality that will be acceptable by the industry, by the standards of clinical researchers, and valuable for humankind to drive what we need to drive.
When I read about the processes or the numbers of things that have been published, those numbers didn’t make sense to me. It takes more than a very small group of people to do what needs to be done to get to that level of quality that is required.
In normal times of publishing and research, there is time to do things. We spend an ungodly amount of time on the data quality, but then there is time for the researchers to run it by peers. COVID-19 was almost the perfect storm for this bad episode, where everyone was running so fast that there was no time for researchers to perhaps do the checks and balances and the validation that they would otherwise do. A lot of people with good intentions. Researchers and physicians spend their career to save lives. They were caught in the middle of that perfect storm and they maybe failed. They didn’t have enough time to do what they need to do to check the quality and validate. It was just happening too fast, and this is where mistakes can happen.
Even within a single institution, researchers are sometimes pressing for data that doesn’t exist in the black-and-white form they expect, with consistent validation and procedure across service locations and across EHRs that fits neatly into a table without requiring a lot of analyst footnotes. How do you turn data from multiple health systems into a reliable source for research?
No two installations of the same EHR will ever be alike. Then you compound the problem by looking at different EHRs, then compound it again by looking at different countries.
We have invested a lot of hours and capital in the past six-plus years to tackle exactly that problem that you said. We have almost a Rosetta Stone in our master ontology. We have a centerpiece, a language that TriNetX adheres to. You take the best standards from all over the world and then go healthcare organization by healthcare organization. It doesn’t matter what you find there — you have to map it into your master ontology.
But this is the beauty of it. By mapping it, you develop a deep understanding of how that healthcare organization is talking, because that’s the only way to map it to something that is more coherent and consistent. That is what we do. It’s difficult, but by doing that, you start to create this standardization abstract layers. The analytics that we build, and all the functions that need to interact with the data, can now speak one language because we’re taking care of the translation. It is a massive investment. It is a core component of what we do.
I’ll give you an example. When COVID-19 happened, old diagnoses for old coronavirus conditions existed in the platform. Very quickly the different regulatory organizations started to release new codes to capture those patients, specifically the COVID-19 patients and tests. We implemented those codes immediately. But that doesn’t mean anything because your hospitals have to report on that as well. We work with an amazing network of healthcare organizations that rose to the challenge in starting to report on those codes.
It’s an informatics and software effort on our part, but it’s also a coding and informatics effort on the healthcare organization’s part. You apply all the quality checks and all the work that we do together as a network to be able to then show researchers and government entities that we’re working the results. These are the patients that we see. This is what they have. These are their profiles. Let’s see what’s working, what’s not working. The utilization of drugs, the utilization of everything. Outcomes. This is the result of massive informatics efforts where all the players have to join forces. It worked very well, it worked fast, and it was on a global scale. Not just the US, but hospitals all over the world rose to that challenge.
What questions should researchers ask to make sure the data that someone else collected is appropriate for their study?
You have to work with reputable companies. We announce the names of who joins our network. We openly talk about the quality processes and the checks that we do. We have hundreds of publications that have been reported on our data. It creates a level of trust. A network of more than 40 industry partners — healthcare organizations, life sciences, and and research entities — have been using us for the past six years and have trust.
A researcher will very rarely go to the record level. No one will let them see that anyway. Even if you looked at the record, do you also want to interview the patient? When you interview the patient, do they even know what they have? At the end of the day, you must trust an organization to create a quality data asset for you. You can audit it if you want. We are very open for everyone looking and auditing our processes, how we look at data, how we do our work. There is a lot around data governance, process, and people that we are very open about. We are open to suggestions and always getting better and better. That creates confidence within the research community to use the data assets that we have time after time.
A lot of research has been published in the last many, many years. A lot of the time, we allow researchers to analyze our data to verify that they can replicate the results that have been achieved through other means. By doing that, you create the ability to validate that a similar set of data on which you run a different set of science and algorithms on it gives a similar conclusion. Or you get a different conclusion, but you can explain the difference. That validates that you can trust this data asset, because time after time, it delivers the answers that you expected, which then gives you confidence to start asking new questions.
Are you seeing impactful COVID-19 research being performed using your platform?
It’s a huge impact. The pharmaceutical industry, contract research organizations, government, and we ourselves are publishing around COVID using our data asset. We are helping find a lot of things that are moving the industry forward in this rapid development of cures. For example, we have published that with COVID, compared to other like conditions, you get more strokes with younger populations. We have validated that assumption. It’s a huge learning, because physicians and the frontline people who are treating those patient now know that in young patients, they need to be on the lookout for other things that could be going on and make appropriate diagnosis and therapy decisions. It saves lives on order of magnitude immediately, not to mention providing insight for those who develop the therapies.
We have many examples of uses of drugs and outcomes that we supported. TriNetX has been in the forefront of fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. That makes everybody who works at TriNetX proud.











































I generally follow AP Stylebook style guidelines: Do not use all-capital-letter names unless the letters are individually pronounced: BMW. Others…