Top News
Blackstone will acquire a 75% stake in Ancestry for $4.7 billion, giving the private equity firm access to the company’s DNA information on 18 million people.
The genealogy company, which launched a consumer DNA testing service last year that it has expanded to include genetic health risks and insights, reports annual revenue of over $1 billion.
Ancestry was valued at $3 billion in 2017 and considered running an IPO twice since then, but faced slumping sales as both it and competitor 23andMe laid off employees. 23andMe has sold the genetic data of its customers to drug companies for clinical studies, an area in which Ancestry lags.
Reader Comments
From Bug Frowner: “Re: Epic’s return to work requirement. Ignores its county’s public health order.” Dane County, Wisconsin’s July 7 emergency order says business “should, to the greatest extent possible” facilitate remote work to minimize in-office presence. Epic is therefore not specifically breaking any law that I can see since the wording is more of a recommendation. I would struggle to return to campus work as an Epic employee if I were high risk and otherwise fastidiously isolating, but we all know that bosses make the rules and our choices are to comply or leave. Media coverage has, as it often does, lapsed into the sensationalistic in portraying the complaints of a tiny percentage of Epic employees as a topic for heated debate into which Internet cheap-seaters feel the need to insert themselves. More interesting to me is that Epic says that only 24 of its employees have tested positive, which seems like a tiny number out of 9,000+ mostly young employees, but I assume they haven’t yet mass tested the folks who will be returning to campus. Judy Faulkner has said the company is working on immunity passport capabilities for its EHR, so maybe they’ll run employee antibody testing even though that has limited value outside of healthcare provider organizations given relatively low overall infection rates.

From Al Lewis: “Re: Livongo’s sale for $18.5 billion. The entire employer community doesn’t even spend $18.7 billion on diabetes-coded admissions. Not even close. Nor have they claimed to reduce that one item, the item that should concern employees the most. And they never explained why they want everyone to test multiple times a day when Choosing Wisely says most Type 2 diabetics are more likely to harm themselves than benefit through overtesting. Meanwhile, as I will be posting in a few hours, the price of insulin is skyrocketing thanks to greedy PBMs and employers aren’t doing a thing about it.” I interviewed Al Lewis, who I titled “workplace wellness skeptic,” a few months ago and asked him for reaction to the acquisition news.

From Donor Here: “Re: matching Donors Choose funds from Tyson Foods and your Anonymous Vendor Executive. Is that still available?” Donors Choose still lists 24 unfunded projects for which Tyson Foods is matching donations 10-to-1 and I still have ample matching funds available from my Anonymous Vendor Executive. Many other projects offer 2x or 3x matching from companies and organizations, which is still a lot of bang for the buck. I just received an email today from middle school science teacher Ms. W in Washington, for which our $32 donation (which was then matched 10 to 1) bought distance learning tools (microphone, graphics tablet, lighting, and a camera mount) as well as a 15% optional donation to fund the work of Donors Choose. She told me this morning that her school just announced 100% distance learning to start and she will immediately use the new technology to retool her her hands-on science classes for home learning. Donation instructions:
- Purchase a gift card in the amount you’d like to donate.
- Send the gift card by the email option to mr_histalk@histalk.com (that’s my Donors Choose account).
- I’ll be notified of your donation and you can print your own receipt from Donors Choose for tax purposes.
- I’ll pool the money, apply all matching funds I can get, and publicly report here which projects I funded, including teacher follow-up messages and photos.
From Live Longo Glen Tullman: “Re: Teladoc acquring Livongo. Paid too much, in a hurry to cash in some of its own overpriced shares.” My thoughts on the deal:
- This is the third-largest acquisition of a US company this year. Teladoc will give $0.592 of its shares plus $11 in cash ($159 per share) to buy Livongo.
- I don’t get the synergy, other than that both companies have to keep employers and insurers subscribing for services their constituents may not use and that may provide minimal benefit.
- The implicit market value of the combined money-losing companies is an eye-popping $37 billion, nearly double that of Cerner.
- TDOC’s market cap is $16.5 billion, nearly quadruple that of a year ago, on just $716 million in annual revenue. LVGO’s market cap is $1.5 billion, eight times that of September 30, 2019 on $207 million in revenue (selling price is 90 times revenue).
- Shares of both companies regained some of their losses Thursday after dropping hard after Wednesday’s announcement.
- LVGO’s Q2 earnings report from Wednesday went mostly unnoticed in the acquisition news, but the company had a good quarter, with revenue up 125%, adjusted EPS $0.11, beating expectations for both.
- Livongo’s executives will pocket fortunes from the acquisition just 12 months after its IPO. Lee Shapiro’s shares are worth around $860 million, Glen Tullman’s around $700 million, and Zane Burke (who joined as CEO just 19 months ago) holds shares worth around $160 million.
- I’m skeptical in general about early-stage companies that sell services through employers and insurers with unproven promises about saving them money, so I’ll simply say (a) good job Livongo for convincing Teladoc of predicted synergies, and (b) good job Teladoc for riding the likely temporary share price bump even as virtual visits slack off and health systems launch their own competing offerings to diversify. I don’t see the value for shareholders, patients, or the healthcare system in general, but then again I’m not a centimillionaire stuffing wads of investor cash down my pants.
Webinars
August 19 (Wednesday) 1:00 ET. “A New Approach to Normalizing Data.” Sponsor: Intelligent Medical Objects. Presenters: Rajiv Haravu, senior product manager, IMO; Denise Stoermer, product manager, IMO. Healthcare organizations manage an ever-increasing abundance of information from multiple systems, but problems with quality, accuracy, and completeness can make analysis unreliable for quality improvement and population health initiatives. The presenters will describe how IMO Precision Normalize improves clinical, quality, and financial decision-making by standardizing inconsistent diagnosis, procedure, medication, and lab data from diverse systems into common, clinically validated terminology.
Previous webinars are on our YouTube channel. Contact Lorre to present your own.
Acquisitions, Funding, Business, and Stock

Nuance announces Q3 results: revenue down 10%, adjusted EPS $0.19 versus $0.20, beating analyst expectations for both. The company said in the earnings call that it has signed pilot agreements for its Dragon Ambient Experience with WellSpan, Boston Children’s, Children’s Atlanta, and Lehigh Valley.

CVS Health beats analyst expectations for Q2, reporting a 3% increase in revenue and adjusted EPS of $2.64 vs. $1.93. Utilization of telemedicine services through its Aetna network and MinuteClinics jumped over 700% during the quarter as patients stayed away from in-person office visits.
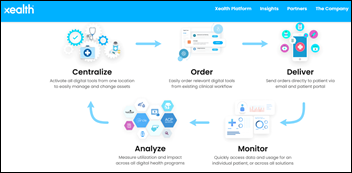
Cerner and VC firm LRVHealth invest $6 million in Xealth, a Providence Health & Services spin-off that has developed software to help providers find and prescribe digital health apps and programs.

Digital point-of-care prescription savings vendor OptimizeRx reports Q2 results: revenue up 25%, and adjusted EPS of $0.02 versus $0.09, beating analyst expectations for both.

CPSI announces Q2 results: revenue down 10%, EPS $0.12 versus $0.12, beating analyst expectations for earnings but falling short on revenue.
Signify Research says the crown jewel that Siemens Healthineers gets in its $16.4 billion cash acquisition of Varian Medical is the latter’s oncology software business, which has $600 million in annual revenue with an 18% year-over-year-growth. The report notes that oncology is positioned at the convergence of EHR, lab, radiology, and surgery systems and the need to collaborate for diagnosis and treatment creates complicated workflows. Elekta is Varian’s chief competitor in that area. Siemens Healthineers is focused on three digital areas — imaging AI, advanced imaging hardware, and lab diagnostics. Siemens Healthineers, spun off from Siemens AG (which still owns 85% of its shares), is among a small group of medical technologies that have more than $20 billion in annual revenue, possibly coming in at #3 behind Medtronic and Johnson and Johnson.
Sales
- Michigan Medicine selects Mach7’s enterprise imaging technology.
- CPSI selects cloud services from Google Cloud.
- The Iowa Health Information Network selects PDMP connectivity, analytics, risk assessment, and patient support technology from Appriss Health.
People

LexisNexis Risk Solutions promotes Josh Schoeller to CEO of its healthcare business.

Industry long-timer Andrew Eckert (Acelity) joins medical claims company Zelis as CEO. Eckert has held leadership positions at Eclipsys, TriZetto, and Valence Health.

Justin Manning (Nordic) joins Evergreen Healthcare Partners as principal consultant and VP of medical device and data integration.
Announcements and Implementations
UHIN adopts NextGate’s enterprise master patient index across its HIE network in Utah.
Redox announces GA of Data on Demand, giving developers the ability to query any EHR or health data sources via the company’s API.

AHRQ publishes an electronic patient-reported outcomes toolkit.
Government and Politics
Politico reports that the VA will re-commence its EHR overhaul with a rollout at an unnamed facility in October. The conversion from VistA to Cerner was halted earlier this year as VA facilities focused on preparing for and treating COVID-19 patients. The VA has switched its go-live plans from facilities in bigger metropolitan areas to those in smaller cities in the Pacific Northwest and Midwest, citing a lack of access during the pandemic to clinical experts who had been expected to help with system customizations for the larger facilities.
Politico also reports that two senators have introduced legislation that would make the post office’s address matching software available to EHRs via API for patient identification and matching.
COVID-19
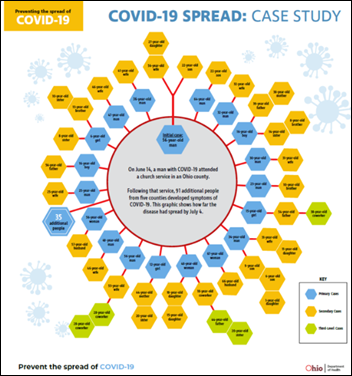
An Ohio Department of Health contact tracing graphic shows how one infected church service attendee spread the virus to at least 91 people in five counties in less than three weeks. The graphic was tweeted by Ohio Governor Mike DeWine, who announced Thursday that he has tested positive for COVID-19 as part of the screening for his now-cancelled Thursday greeting of President Trump in Cleveland.

Virginia launches the Covidwise app, becoming the first state to launch an exposure notification app using technology from Apple and Google. The app notifies users if they come into contact with other users who’ve tested positive for COVID-19. Some public health experts have questioned the effectiveness of such apps, citing low and thus ineffective adoption rates, privacy concerns, false alarms, and a lack of nearby testing capacity.
University of Miami Health System launches a remote patient monitoring program for discharged COVID-19 patients using TytoCare home health devices.
The Harvard Global Health Institute and Google Cloud develop COVID-19 Public Forecasts, a free planning resource that offers healthcare workers 14-day projections of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths by county and state.
An MRI review of 100 recovered COVID-19 patients who had no pre-existing cardiac conditions — most of them who had experienced only minor COVID-19 symptoms and recovered at home — finds that 78% have cardiac involvement and 60% have ongoing myocardial inflammation. The authors conclude that cardiac involvement is unrelated to COVID-19 severity and warn that undetected inflammatory disease may present a large health burden in people who think they got over COVID-19 without incident.
The National Institutes of Health forms the Medical Imaging and Data Resource Center, which will use AI and machine learning to develop new diagnostic tools clinicians can use to better care for COVID-19 patients.
The New York Times explains how the US uniquely failed to control COVID-19:
- A tradition of prioritizing individualism over government restrictions, which has also saddled the country with a world-lagging and unequal healthcare system.
- Lack of effective travel restrictions in excluding from the ban the family members of American citizens and permanent residents returning from infection-ravaged areas, failing to address the infection’s spread to Europe promptly, exempting the UK from travel limitations, and failing to create a quarantine process.
- Lack of state travel restriction enforcement.
- Testing delays caused by the CDC’s distribution of faulty tests that it insisted be used over tests that were developed in other countries.
- Commercial labs charging patients for COVID-19 testing, which discouraged their use.
- Conflicting public mask advice from WHO and CDC, some of that based on the need to prioritize the limited supply of them for healthcare workers, and allowing masks to be turned into a political symbol with partisanship as its most accurate predictor.
- The push by federal and state governments to reopen the economy with the virus still uncontrolled, which caused outbreaks afterward and provided only a brief recovery as personal fear and unemployment caused people to limit spending anyway.
- Mixed and confusing messages from political leaders and partisan news media, including distributing medical misinformation and expressing unwarranted optimism.
Other

HIMSS hires a second Australian Digital Health Agency executive as CIO Ronan O’Connor joins former CEO Tim Kelsey. O’Connor’s new role was not specified, but Kelsey became SVP of HIMSS Analytics International in January 2020.

HIMSS will continue to publish the mobile health app best-practices guidelines of Xcertia, a now-dissolved project of HIMSS, the American Medical Association, the American Health Association, and DHX Group. The Xcertia standards body was formed in December 2016, last updated its guidelines in February 2019, and then went silent shortly afterward. The organizations haven’t announced why they pulled the plug. The three principals of non-profit app curation organization DHX Group seem to have moved on to other projects.
The local paper says that at least 13 Epic employees claim that the company has demoted team leads who expressed concern about its plan to bring employees back to campus, which Epic denies.
European Union authorities will investigate Google’s acquisition of Fitbit, worried that Google will target ads based on the user fitness data that Fitbit collects. Google says it has no such plans and has offered to sign a contract that limits its use of the data. A consumer group concludes, “It is hugely important that the E.U. carries out this in-depth examination because wearable devices like Fitbit’s could in future give companies details of essentially everything consumers do 24/7.”
Sponsor Updates
- InterSystems launches T2020, the latest version of its TrakCare EHR, which includes COVID-19 functionality, an enhanced user experience, and a unified workspace for patient records and documentation.
- Cloud Computing Outlook names Goliath Technologies a Top Virtualization Solutions Provider.
- HCI Group Chief Digital Officer Ed Marx publishes a new book, “Healthcare Digital Transformation: How Consumerism, Technology, and Pandemic are Accelerating the Future.”
- Spok announces that all 20 adult hospitals and all 10 children’s hospitals named to US News & World Report’s 2020-21 Best Hospitals Honor Roll use Spok clinical communication solutions.
- Saykara’s voice-enabled mobile AI assistant is named as a healthcare innovation awards finalist.
Blog Posts
Contacts
Mr. H, Lorre, Jenn, Dr. Jayne.
Get HIStalk updates.
Send news or rumors.
Contact us.







![image[88]_thumb image[88]_thumb](https://histalk2.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/image88_thumb.png)
















![image_thumb[59]_thumb image_thumb[59]_thumb](https://histalk2.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/image_thumb59_thumb.png)


![image[94]_thumb image[94]_thumb](https://histalk2.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/image94_thumb.png)













































 .
. 

I generally follow AP Stylebook style guidelines: Do not use all-capital-letter names unless the letters are individually pronounced: BMW. Others…