Today's post contains the phoenixes rising from the ashes of the post COVID telehealth era. There's two things that destroy…
Healthcare AI News 1/28/26
News
OpenAI introduces Prism, a free ChatGPT-based workplace for scientists to write and collaborate on research.
A Louisiana news site reports that LCMC Health has removed its patient consent disclosure stating that it uses Nabla for ambient documentation. The organization’s compliance department determined that patient consent is not required for other types of note-taking and therefore is not needed for an AI scribe. Louisiana law requires only one-party consent for audio recording, which in this case would be the provider.
Testing finds that the latest version of ChatGPT cites sources that were themselves generated by other AI tools, including Elon Musk’s AI-created encyclopedia Grokipedia, which has been accused of promoting right-wing narratives on controversial topics. Experts question whether AI tools can be trained to ignore AI-generated content that may be incorrect, leading to recursively less accurate information. When asked by a news outlet about a fabricated quote that was attributed to the site, an XAI spokesperson responded, “Legacy media lies.”
Business
The Guardian warns that Google’s AI Overviews could pose a public health risk because they summarize search results that may be inaccurate or low quality. A study of health-related queries found that AI Overviews rely heavily on content from Google’s YouTube that anyone can upload. Experts caution that users may accept the summaries at face value, and that even when summarizing medical literature, the tool can’t assess the quality of research.
Research
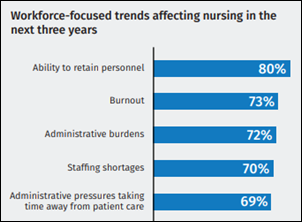
A Wolters Kluwer survey finds that 58% of nurses use generative AI in their personal lives and 46% at work. Nearly half believe that AI could reduce nurse burnout by automating documentation, triaging patient questions, and streamlining workflows, while 62% say that using AI for onboarding and training can get new nurses onto the floor faster. Most report that their organizations lack formal AI policies or training.
A small UCSD Health study finds that clinicians generally view Epic’s EHR-integrated LLM chart review tool as useful for summarizing patient records, even though it frequently misses relevant details and occasionally hallucinates, requiring careful human verification. The authors conclude that such tools can augment workflows, but are not reliable enough to be used without clinician oversight.
Researchers believe that agentic AI systems could help hospitals prepare for extreme climate events that fall outside of emergency planning assumptions.
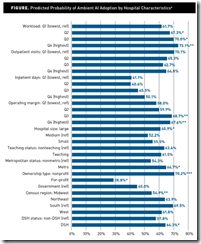
A study finds that of the 42% of US hospitals that use Epic, 62% have implemented ambient documentation. Adoption was significantly higher in metropolitan and government-operated hospitals and much higher in non-profit versus for-profit hospitals.
Other

ChatGPT Health gives the Washington Post’s technology columnist an F for cardiac health after analyzing a decade of his Apple Watch data, a conclusion that his physician and Eric Topol, MD, say is wrong. When he repeated the test with Anthropic’s Claude for Healthcare, it assigned a C, although both tools changed their grades when he repeated the same question. He also notes that his resting heart rate reports a significantly different number each time he upgrades his Apple Watch. Topol concludes that, “You’d think that they would come up with something much more sophisticated, aligned with the practice of medicine and the knowledge base in medicine. Not something like this. This is very disappointing.”
Contacts
Mr. H, Lorre, Jenn, Dr. Jayne.
Get HIStalk updates.
Send news or rumors.
Follow on X, Bluesky, and LinkedIn.
Sponsorship information.
Contact us.



“…right-wing narratives”? I really appreciate your blog. I have for many years. But can you include less politics in the blog?
Politics is a real thing that has real impacts on our industry and the world, as much as people like to pretend that it’s all just a fun intellectual exercise.
Elon Musk says he created Grokipedia because Wikipedia is “woke.” Analysis has shown that 85% of Grokipedia’s content was grabbed directly from Wikipedia, then tweaked where his team disagreed with wording or analysis. That is relevant to the news item I mentioned because it will double weight Wikipedia information as a near clone of it, then add a specifically contrarian point of view as a site whose reason for being is specifically to do that. I would argue that neither source should be used for AI training since by definition, neither contains anything original and instead just references someone else’s source material that the AI can see directly without requiring someone else’s summary.
The important part of the story is that AI is being trained on AI generated information that exists solely to copy another site’s supposedly factual information except where it disagrees with it. If AI is to be trusted to provide health information, the sources it learned from are important.
I remember when the COVID lab leak theory was a “right-wing narrative”
Move your quotes to where they should be and it’s no longer politics-in-the-blog, but instead a fact that’s true at face value:
“which has been accused of promoting right-wing narratives on controversial topics”