From JJ Canuck: “Re: Oracle. I was visiting the Oracle booth (was trying to figure out their integration engine story … which is ‘coming out.’) The sales guy said they will announce a ‘big deal’ in the next week or so about a partnership with a ‘big vendor’ that will provide badly needed HIE capabilities and some other vague set of features. When I asked if it was Cerner, he just smiled, giving me the indication that I had made a good guess. Sore feet and off to Universal for the last wonkfest. Maybe I’ll throw-up that $9 bean burrito I had at lunch on the roller coaster with Neal Patterson sitting behind me. Daydreamin’.” You remind me that I forgot to complain about predatory convention center food pricing: a soda out of the machine was $3.25, a chicken salad sandwich was $9, and a banana was $3. That last one’s especially maddening since I buy a big bunch of them at Sam’s for half that amount.

From Jay: “Re: best marketing tee shirt ever. From backup vendor Mozy’s booth at HIMSS.” It’s a bit of a stretch, but almost funny. I tried their service a few months back and it was a pig on my PC, so I removed it and went with SugarSync.
From Andrea: “Re: HIStalk. LOVE LOVE HIStalk, you, and Inga. How would a small biz like us (VAR) compete with the big bad vendors unless we had inside dirt on them? Keep up the fantastic work and have fun at HIMSS!” Thanks — we love you right back.
From Fred: “Re: Meditech. Announced on Saturday that they would be getting modular or near modular certification for their HIS software. They reported that it just required some paperwork and would be completed soon.” I’ll mark this as Unverified since I was given related information off the record a couple of weeks ago.
From Leotards: “Re: Noteworthy. That’s a snarky comment made by an underperforming mid-level manager or sales rep no longer with CompuGroup Medical, I presume. Rick Mullins is gone; there’s been quite the shakeup of the existing C-suite amongst all the companies CompuGroup Medical US is merging into a single entity. Supernumerary chiefs of all stripes are being relieved of their individual fiefdoms as NoteWorthy,Healthport, Visionary HealthWare and Antek HealthWare are all subsumed by CompuGroup. Sweeping positive changes have been instituted, our flagship products are being strengthened and developed, and all this accomplished without sending out huge swaths of pink slips as sometimes happens with these acquisitions. I’m just a field rep in the trenches, but I’m quite pleased to now be part of CompuGroup Medical.” Unverified.
From J.B.: “Re: Meditech. The Meditech/LSS deal is finalized. They still haven’t straightened out any arrangements of staff, but LSS is still going to be called LSS. It is now a ‘wholly owned subsidiary’ of Meditech.” Verified – Meditech has posted the news on their site.
From Dichotomy: “Re: HIStalkapalooza and sponsor lunch. You have to repeat these in Las Vegas! It was really great meeting together.” We’ll see how it goes, but I would definitely like to do both again. It was really nice (but nerve-wracking, especially for Inga) to briefly say hello to our sponsors and for me to be flanked by those lovely and whip-smart (but suddenly mute) ladies. Since I almost never see actual HIStalk readers in person, I asked for a show of hands of how many people felt they knew Inga, Dr. Jayne, and me personally even though we haven’t met. A surprising number of hands (a majority, I’d say, maybe more than that) went up. That was gratifying since we definitely feel connected to our readers and sponsors whether we’ve met them or not. I’m glad that comes across.
From Tech Doc: “Re: innovation. Saw Napochi at HIT X.0 Geeks Got Talent on Monday. Showed a 3D body module of their EMR used to map IVs and such which integrates with their flowsheet and physician note. Didn’t find a booth, but their website has a video of them demoing a touchscreen whiteboard replacement. Pretty neat stuff.”
From Kate the Sponsor: “Re: HIStalk. I just wanted to say thank you for the wonderful events at HIMSS! I really appreciate what you both do. HIStalkapalooza was a blast, loved the venue. I got there a little late, however, and missed the awards – are you going to post the full awards section on the site? I did see the highlights in the video Inga posted which were great. I’m sorry I missed the hilarious red carpet commentators — I felt like I was watching E! I also really enjoyed the sponsor lunch yesterday. It was great to break bread with fellow HIStalk fans and sponsors, but really the true highlight was having the three of you make an appearance. And, Inga, the handwritten thank you notes were so sweet. That must have really tired your hand out to write all those yourself, but the personal touch was really special. Thanks again for all you do for the industry, looking forward to next year!” Thanks for those nice words. I’ll get the HISsies list up when I get back to the comfort of a full-sized keyboard and dual monitors since there’s a lot of typing involved. I hope the lunch attendees whose notes were written by me (Inga and I split them) could read them since my handwriting is pretty bad. I said there that we are proud to be amateurish and my handwriting is a testimonial to sincerity backed by a total lack of polish.
From Suzanne: “Re: HIStalk. No doubt you are inundated with work, e-mails and miles and miles of walking this week, but I just wanted to send you a quick note to thank you for a great lunch today (and great party last night). We are thrilled to be new HIStalk sponsors – and not just because of free food and drinks! As a small, newcomer vendor in a tiny 10×10 booth at the far end of the hall and among the ocean of booths at HIMSS, it has quite literally been amazing how many people have come up to us, saying they have specifically sought us out. When we ask how they have heard about us, many have said through HIStalk. I was a little skeptical of advertising on HIStalk at first, thinking that the majority of readers may be vendor types, but that is clearly not the case.” Thanks – you are too sweet. We won’t recommend a product we haven’t used ourselves, but we will get readers the information they need to allow them to qualify their own interest. I’m happy we can do that since it benefits both vendor and prospect. According to the survey I just finished, 83.4% of HIStalk readers say they have a higher level of interest in companies we’ve written about. That’s flat out amazing and we don’t take that responsibility lightly.
For me and many/most attendees, the HIMSS conference is over. Maybe you’ll see Michael J. Fox flying into MCO as you are flying out since he gets to speak to the few folks sticking around for Thursday sessions.
Tomorrow is traveling home day, and while I’ve really enjoyed being here, I’ll be even happier to get back to my familiar routine, PC, and wife. A ton of people were sitting in the grassy area outside the Lobby C area of the convention center this afternoon. It looked like a capitalist Woodstock as attendees in suits sprawled awkwardly in the grass (I saw one guy fully face down on the lawn, suit and all, reading a book). I bet most of the impromptu sunbathers were heading back to snow and gloom and figured they’d better get sun now or else wait a couple of months for it to find its way back to them.
The weather was good today — it’s a perfect and breezy 78 as I write this close to sundown and kids are having a ball in the pool right outside my window. Walking back to my hotel, I could smell wood smoke from a steakhouse, blooming flowers, and a little tang of ocean salt in the air. For most folks going home, they’re going to be smelling smoke from the fireplace, flower-scented air fresheners in closed and airless rooms, and salt from the treated roadways. No wonder people like to vacation here, even though Orlando is culturally bankrupt, jammed with traffic, and filled with people who’ve lived her for decades and yet won’t quit calling New York and Ohio “home.” Those are issues that only the locals care about.
I’m behind on e-mails from the traveling, the conference, and our events, so bear with me as I try to catch up this weekend. I think people sometimes forget that it’s just me on the other end and I’m working a lot of hours.
Here’s the bad news for all you folks (including me) who are proudly taking new iPads home won as prizes this week: the iPad 2 comes out next week, so that new one you bagged this week is already obsolete even before you even get to strut it in front of your admiring families. Doh!
I got some e-mails from execs of some of the vendors I mentioned yesterday as ignoring my “I’d like a demo” booth body language to give them a second chance. I did so today, with mostly the same results. I should mention, however, that my title and hospital name on my badge wouldn’t necessarily make me a likely candidate, although the small font size makes it unlikely that they ignored me for that reason. Today was the last exhibit day and nobody was paying much attention to those of us still roaming the exhibits late into the afternoon. Mostly I saw reps talking on the phone or sitting together in their couch / table areas making dinner plans or cursing as they spoke animatedly among themselves (I’ve noted that young, male sales reps seem to curse a lot in each other’s company – it’s like using profane emoticons).
And speaking of that, I also do not identify myself to vendors, even those I exchange e-mails with or those who tell me to ask for the CEO or other executive personally. I’m a mystery shopper – I want to be treated exactly the same as anybody else (or as me in my day job role).

Our King and Queen judge Greg Wilson from Salar got this picture today with John Templin and his long string of badge ribbons. I’m not sure Greg knows the history – John does this every year, usually as he’s trying to raise money for the HIMSS Foundation. You saw him on stage this morning as the keynote started.
A CapSite survey finds that 23% of hospitals plan to use consulting help to get their clinical systems up and running.
Franciscan Alliance will roll out Epic at its 13 hospitals and 165 practices. The cost: more than $100 million over the next two years.
UK Healthcare will implement Allscripts EHR/PM and integrate it with a new version of its Sunrise inpatient EHR.
Jordan Hospital (MA) lays off four managers (IT, quality, pharmacy, and diagnostic services) and VP/CIO Dennis Fonseca.
New PatientKeeper CPOE customer: Madison Memorial Hospital (ID). Going live on the same product: Ashe Memorial Hospital (NC).
CollaborativeCARE Conference signs a deal to bring in HIMSS to run a one-day education program during its first conference this coming November.
Wednesday Keynotes – Kathleen Sebelius (HHS secretary) and David Blumenthal (national coordinator)
- I don’t know if I’ll ever get used to Steve Lieber’s spiked-up hair, which I noted as he read a suck-up HIMSS proclamation honoring Kathleen Sebelius for taking money away from taxpayers and giving it to much richer vendors and doctors.
- It’s a given: everyone in politics and government will always publicly praise their wise, hard-working, and selfless bosses (Sebelius-Obama, Blumenthal-Sebelius).
- Sebelius said that of 231 vendors of certified products, 2/3 of them have fewer than 50 employees, and “any one of them could be the next Google or Microsoft.” Really? With 230 competitors and few takers for most of them until the Cash for Clunkers EMR program came along? Maybe she meant the next Google Health or Microsoft HealthVault.
- She talked about the country’s health. I’d still argue that EMRs just make the treatment episodes arguably more efficient. It’s what people do when they’re not sitting in front of a provider that’s expensive. Someone should create a business model for wellness and population health. She didn’t mention any of those things.
- She said you can’t just advocate the technology – you must advocate an improved healthcare system.
- She lauded Blumenthal’s “doctor perspective” (he supposedly still sees the occasional patient, although he’s had muckety-muck Harvard jobs for so long it would be interesting to see how many and how well).
- Blumenthal was a pretty good speaker, just a bit quiet and monotonic and very careful with his words (I actually liked his style). He said he was naïve about what could be accomplished at last year’s HIMSS conference.
- He said 21,300 providers have signed up as Meaningful Users and $20 million has been paid out under Medicaid. The Medicare payments will start in May.
- He said the timetable for Stage 2 will be challenging, but reasonable and achievable.
- He cited 62 Regional Extension Centers enrolling 6,000 providers each week.
- He said that colleges have trained 3,400 people in HIT and the goal is 10,000 per year.
- “HIE is a team sport that requires local coaches.”
- He said the system was deficient in quality measures, population health, clinical decision support, and interoperability.
Exhibit Hall and Session Notes
- A reader asked me to check out Lawson. They were pitching ACO support, Cloverleaf, scheduling, HR management, and ERP. Their booth was pretty dead, but it was a bit early. They had coffee and popcorn. The booth looked nice (curvy yellow sofas and quiet demo areas) and the wall posters made it clear they have a lot of products. I can’t say I had a reaction either way.
- Another reader asked me to stop by Candelis Astra, which offers some kind of workflow cloud solution stuff for radiology and images. That’s all I know because of the five reps in the booth, two were on their phones and the other three were sitting around a table deep in their own conversation. One did pop around the corner and ask if I wanted a demo, but I was committed to walking away at that point. Still, they did ask, so I give them credit for that – I was just being stubborn.
- I dropped by Clairvia and still didn’t get much attention, but the over-the-shoulder demo I watched looked really strong and a big competitor admitted that when it comes to clinical scheduling and acuity, Clairvia is better. It’s a slick-looking product.
- I talked to one vendor’s rent-a-booth-babe. She says she likes HIMSS because it’s conservative. I asked what that meant and her answer was basically that this week’s vendor-employer didn’t make her come in nearly naked. Apparently vendors often do.
- The OnBase magic guy is the best ever. Not only is he funny and really good at riffing (“Step closer, the trolley is coming … I just saved your life, dude”), he even knew a lot of product stuff, like when someone from HP was there and he knew details of OnBase’s partnership with them. I keep thinking maybe he’s an employee who just happens to know magic, but if so, he’s darned good.
- NCR had their HIStalk sign out. I played with their wayfinding kiosk and it was cool. The rep played me perfectly, letting me poke around while offering just enough conversation to make me feel engaged
- A reader asked me to find out what Epic’s Canto runs on. It’s iPad-only, the rep told me. I have to say those Epic kids are really pleasant and helpful.
- I like the big sign on Healthland’s booth: “We’re not for everyone – bringing a certified EHR to rural hospitals.” Bravo – how many companies would just leave it wide open in the hopes that Cleveland Clinic or someone like them might get fooled into buying it? I admire helping prospects qualify themselves. Well done.
- Orchestrate had their HIStalk sign out – thanks! I saw President Charlie Cook there.
- I looked over someone’s shoulder at Shareable Ink and it seemed pretty cool, but I didn’t really get to see any of the form-filling part, just the end result.
- A reader (or maybe it was the vendor – I forget) asked me to drop by Proxense, which does proximity-based security, I think. I’m guessing because the rep said hello and nothing else, so I did the same. I checked out their Web site and it’s not very well designed (note the hover text over the Sales menu item that says “some sort of tagline about sales.”) and makes it hard to figure out what they do. They’re probably engineers from the looks of things.
- I stopped by HT Systems/PatientSecure several times and was anxious to see their palm biometrics in action, but that didn’t happen. There was some other company’s business development guy hogging their time (talking rather than listening). I think I would have saved that conversation for non-exhibit hours if I were him and if I were the company, I’d have some video or something since it’s a highly visual product and a conversation-starter (or so I assume, not having seen it). I’m pretty sure it’s cool.
- I watched a theatre presentation of Nuance’s new Healthcare Development Platform. It sounded interesting: products connect via HTTPS to Nuance to run speech recognition (support provided for iPad/iPhone/iPod Touch OS, Windows Mobile, and any browser). Five lines of code turns a text box into a speech recognition field that then runs its Clinical Language Understanding to extract structured data and map it. They’re offering a free 90-day developer’s license when it goes out of beta in March or April.
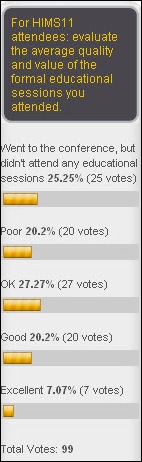
- The only good educational session I attended during the entire conference was today, a really good one on medication barcoding. It’s what you always hope for but rarely get at HIMSS – one guy describing in super-concentrated form all the problems his hospital solved when rolling out medication barcoding. I’ve never seen a session that was so meaty, full of real-life pearls, and pleasant to watch. The pocket guide says only Session 165, Still. Whoever Still is, kudos. No self-indulgent posturing, no fluff, no teasing in the hopes you’ll hire him or his company to finish the story – just really good experience shared. People actually clapped and meant it and the audience questions, instead of the usual droning pontificating, were insightful and on point. My faith in humanity was restored.
- A reader asked me to check out Success EHS, a Birmingham-based PM/EMR vendor. Like almost all Southern vendors, they were very nice and friendly. The product didn’t look all that much different than other EMRs, but it does run the MEDCIN engine and it had a cool Meaningful Use dashboard that shows real-time stats on how individual docs or groups are doing in hitting their numbers. Most impressive is that they charged nothing for that module or any of their Meaningful Use upgrades. I mentioned that I’d won an iPad and the young lady rushed off to give me a super-nice case for it, saying, “I bet you didn’t win one of these.”
- I dropped by former sponsor Apelon thinking I could find a few nuggets to mention just to be nice, but they didn’t have much to say.
- A pretty cool guy from Software AG skillfully pulled me from flowing exhibit traffic to chat. They’re the company giving away the electric guitar that Inga was bragging on playing. They have a rules-based SOA integration platform that can monitor streams of data and do trending and alerting. It’s a platform aimed at vendors and technically astute hospitals and I didn’t understand all of it, but they gave me a couple of cool books that I’m going to read: Process Intelligence for Dummies and SOA Adoption for Dummies.
- Siemens roped me into a five-minute 3D demo of Soarian that was a complete waste of time (and maybe not even a demo since I don’t recall seeing actual screens). The glasses were kind of cool, but the only 3D effects were some lists and video clips that looked like they were floating and the guy narrating live was a bit too over the top for me. It also seemed to be of the “we suck less than before” variety, proudly listing #2 in one category, “improving” in another, etc. I would have worked harder on the message and less on the medium.
- The best thing I saw all conference was Medicomp’s Quippe (pronounced “quip”, by the way), which I checked out only because Inga, Dr. Gregg, and Dr. Jayne were all raving about it and I figured I was the guy to neutralize the Kool-Aid (or IngaTinis) they’d obviously been given. Didn’t happen: it was way cooler than they said. It’s really iPad optimized, allowing dragging templates over to the work space, supporting insertion of pictures with a variety of annotation tools, and some proprietary gestures that are really cool. For example: drag on a vital signs table, write 101.5 with your fingertip on any blank part of the screen, draw a little L over the temperature field, and your 101.5 is instantly converted to text and dropped into the box (or you can use the on-screen keyboard if you’d rather). I don’t know much about ambulatory systems, but what impressed me most is that when you choose a given symptom, tabs open up unobtrusively that show previous encounters for that patient in which those same symptoms were reported. It’s just a very dynamic, fluid app that really wouldn’t work as well on a non-tablet platform. I’ll not call it a “game changer” since my cohorts have overused that phrase when referring to it, but I’ll call it as ingenious and as physician-friendly as anything I’ve ever seen. I saw another vendor’s implementation of the current MEDCIN engine and it was nice, but not in the same league (that vendor confided that they can’t wait to get their hands on Quippe to add it to their product).
E-mail me.
HERtalk by Inga

From The HIStalk Queen: “Re: HIStalk queen contest. My name is Janet Skinner from Skinner and Associates Executive Search and thank you! I won the HIStalk Queen contest and I wanted to thank you very much for the nice IPod Touch prize! Wanted to thank Dave Lareau and Medicomp for a fantastic party! Fun idea to include the shoe contest (what woman doesn’t love shoes?!) and the IngaTinis were fantastic, as you warned they would be. I must have had more than one if I pulled off winning the queen contest, but I think the group I was sitting with had a few too many IngaTinis of their own and their loud cheering tipped the scales in my favor. Would love to see the Histalkapolooza an annual event, great fun… and again, thanks so much for inviting us!” Hard to believe this was our fourth HIStalk party (though the first HIStalkapalooza).

Bill Fera, MD, of E and Y was our HIStalk King.
From Your Fan: “Re: Red Carpet Gals. The red carpet greeters are my CEO Jennifer Lyle and account manager Kara Heward of Software Testing Solutions. As a matter of fact, Jennifer won the Inga Loves My Shoes sash last year and still proudly displays it in her office. They had a fantastic time with the HIStalk readers who were great sports and the Medicomp men in the tuxes would have made Stacy & Clinton proud! We’re glad you had a great time and can’t wait to join you next year.”
The only way our shoe judge Lindsey of RelayHealth could have been more cute here was if she’d had more sleep Monday night and if you could have seen her gorgeous shoes.

Kronos: seriously, at least 100 people were in line trying to win one of the five iPads. I feel badly that I won one seeing how many people would have liked to win.

I shared a cab with the NextGen artist guys!
Assessments for the day:
- BlueCat: girls in cat woman suits. Really? I suppose they really looked fabulous and I am only jealous that I can’t pull it off like they could.
- David Blumenthal: watching paint dry probably could have been more exciting than listening to him as a keynote speaker.
- Meanwhile, Katherine Sebelius (who I swear was wearing the same suit as she does in all her head shots) was explaining to HIT professionals what healthcare reform and ARRA meant. Really? The place was packed and some folks had to watch on closed-circuit TV from the hallway.
- Thank you MEDecision for the Starbucks coffee. It was worth the 20-minute wait in line just to overhear Practice Fusion CMIO Robert brag that the company now has 70,000 users.
- The OnBase heckler was pretty good. He called out the “lady in pink” to come over and hear his deal. Very fun.
- IDS: good job and giving me the one-minute pitch you do.
- Pulse guy (who just started shaving last week): ask who your audience is before you start explaining why buying an EMR today is important. Most of us already are pretty familiar with Meaningful Use.
- From one very smart CEO: I figured out how much it cost us per hour to have people here and it is about $7,000. They better be standing on the corner of the booths trying to sell and not checking messages on their smart phones. Good advice that a lot of vendors should have heeded, including some that I kind of wanted to check out. Like CattailsMD, Azzly (the second time I came around), Wavelink, and a dozens of others.
- Thank you, Sage guy, for showing Health Unity. Yes, I noticed you looking at my shoes because you suspected I might be Inga. Integration is not all there yet (those blue screen errors are a dead giveaway) but the embedded integration will be cool.
- George at Sophos: I couldn’t pronounce your sexy Greek last name, but you were adorable.
- I loved the fondue at EDS. Wish more exhibitors (like Meaningful Use Monitor) had bottled water.
- Ingenious Medical: nothing like having a cute girl wearing high heeled blacked boots to bring in the crowd. Definitely not practical for a three-day show, but who the heck cares?
So much more to say, but Mr. H is ready to post. I will do my best to read my cryptic notes and share more tomorrow.

E-mail Inga.
EPtalk by Dr. Jayne
And now the end of HIMSS11 is upon us. I was surprised to see the exhibit hall as full as it was today. Usually by this point, folks are losing stamina, but at least around the noon hour there was still a veritable sea of navy blazers. I did see several ladies sporting running shoes with their suits, and although I stuck it out in the comfy yet stylish heels, I was a bit jealous.
I also saw quite a few people sporting the bright yellow clog slippers given out by ChipSoft. I stopped by to try to get a pair to mail to Inga as a gag gift, but was turned away empty-handed by the less-than-pleasant rep.
Several of you e-mailed over the past couple of days with thoughts on booths I should visit. I’m sorry I couldn’t get to them all. I gave preference to those that had a hook for why physicians would benefit from their products vs. those that just said, “Hey Jayne will you make an appointment with us?” It’s hard to make appointments when one is anonymous.

I ran into an old friend of mine, Vendor Boy, and asked him, as a veteran, what was the best thing he saw at the show. First place: the Epic booth. Second place: the kilt girls.
I agree with what Mr. H said yesterday. Many of the reps seemed tired and/or bored and some didn’t seem to care whether I was interested in talking about their products or not. I would have thought that with the badge scanners and RFID tracking there should have been some kind of “CMIO with purchasing and decision-making authority” alert like a Bat-Signal in the sky that could have shocked them back into action, but alas, several flat-lined. However, there were notable exceptions:
- OnBase, which does document management. With their sports bar theme, they were happy to tell me about their solutions. Our friendly bartender/rep was happy to show an iPad app that I didn’t see yesterday, which allowed quick on-screen approval of documents including annotation.
- Sage, which had a better showing today than when I tried to visit on Monday to see their new HIE solution.
- NCR, which was giving away autographed copies of the Newt Gingrich book Paper Kills 2.0 as a special HIStalk reader perk.
- Up to Date, which tried valiantly to entertain me while I waited to talk to a specific rep who I heard had a great story to tell, although I got pulled away and never did get to meet him.
I visited the 3M booth several times to try to find out about the new mobile app they told Mr. H they were launching. The people I talked to didn’t seem to know what I was talking about, but they did tell me about their coding support product that uses natural language processing to trigger patient care alerts from dictated text in EHR. Since I’ve seen a lot of care coordinators being let go recently (which seems short-sighted with Accountable Care breathing down our necks) that might be handy, but if that was supposed to be the mobile app, I’m not sure how mobile it was.
Personally I haven’t had good luck with the voice recognition software for mobile devices and most of our hospitals still use traditional dictation systems, so it’s not like the doctors are dictating daily notes directly into the system as they round.
TeraMedica had the guys in the colonial outfits with the tri-corner hats again today. Not sure how that plays with data migration, but they looked like they were having a better time than the ones who were in the booth on Monday.
I gave them a couple of days to spiff up, but Alcatel-Lucent still hadn’t ironed the white coats of the faux clinicians gracing their booth.

Emdeon awarded the iPad from their HIStalk reader-only drawing. The winner was very excited and even sent me a photo of the cute gift bag they packed it in. I’m always happy when someone goes beyond the expected, and delivering to the winner in style is much appreciated.

Props to the Hilton who accommodated my late check-out request and even smiled while doing it, allowing me to spend precious minutes poolside before I head back to the sleet and freezing rain that is surely covering my car. Maybe they could drive me home in this.
That’s a wrap for HIMSS11. See you next year in Vegas, baby!

E-mail Dr. Jayne.
Dr. Gregg Goes to HIMSS
By Gregg Alexander
“It’s late and I have a huge headache (no, I don’t drink, so it’s not a HIStalkapalooza leftover,) so I hope my observations come through better than they feel through the throbbing behind my eyeballs.”
OK, that’s how my post for Monday night would have started if I had not somehow hit “Minimize” instead of “Send.” I awoke Tuesday morning wondering why my post was absent and found that the headache cloud had somehow short-circuited me more than I knew.
So now it’s about 1:00 AM on Wednesday morning and I have just gotten back to snow-covered Ohio (I have a practice to run) and out of my HIMSS suit. I see Mr. H, Inga, and Doc Jayne have already posted for the night while I was traveling, so I’ve again missed out. (Sigh.)
So, this’ll be a mishmash of Monday/Tuesday and since I’m not, as I’ve said, a real reporter, I hope you’ll forgive my mark-missing tardiness.
MONDAY
HIStalkapalooza was a ball! Mr. H and Medicomp built upon the great groundwork laid last year by Ivo Nelson and Encore with the friendly venue, excellent food, free drinks, and a rockin’ venue. The red carpet entry, the HIStalk limo rolling up and down, and the Batman-sign-esque HIStalk light on the wall across from BB King’s set a superb tone for J. Bush, Dave Lareau, John Glaser, and the Insomniacs to rock the house all the way out. (Seriously, the red carpet entry and the gorgeous and funny red carpet interviewer ladies would have made even Billy Bush proud.)

The HIMSS opening session left me sort of … well, I actually left it, so I suppose that tells you how much I felt I was gaining. The typical HIMSS HIT rock show multimedia wasn’t enough to make the retread of “look how much we’re doing for the world of healthcare” seem worth enduring … again.
The 1,000-plus exhibitors made it appear that the economic downturn is over, at least in the HIMSS-associated halls. Exhibits stretched for what seems like a mile and from floor to ceiling. In fact, with so many vendors flying banners, signs, and rotating “come-see-mes” from the exhibit hall rafters, they all sort of drown each other out and it makes it seem like less of a good idea. I mean, if it doesn’t help people see where you are from across the vast exhibit hall stretches, is it still a helpful way finder device?
I got to enjoy many great conversations with tons of vendors and noticed one really impressive thing throughout: not once, not one single time did any one of them mention Meaningful Use during any of the conversations. It is possible my ears have started to become numb to it, but I’m pretty sure none brought it up. Not exactly sure what that implies, but I did enjoy the respite.
Loved the MED3000 demo of their incorporation of Medicomp’s Quippe tool. Providers – if you haven’t seen it, you should absolutely make the effort to check it out at either MED3000, Pulse, or especially the Medicomp booth where you might actually have a chance to walk away with a free version of it on a free iPad. I think it is perhaps the first, honest-to-goodness game changer (I see where Inga used this same term in her Tuesday night post) in the world of HIT to come down the pike since Larry Weed. Indeed, Dr. Jay Andres at MED3000 told me every single provider he’d shown it to had all made the exact same queries after seeing it: 1) How soon can I get it? and 2) Is it really as easy as it looks here?
RemitDATA has become a big HIMSS sponsor and has a pretty cool offering (at a GREAT price point) to help docs evaluate the financial side of their practices. Sort of athenaCollector-ish, but from multiple data capture sources.
Thomson Reuters is working on some great stuff for health education (and more) and also has some of the nicest people!
Soapware’s Randall Oates has a great new approach to the medical scribe concept: the Medical Coordinator. The MC sits in another room and listens in to a patient-provider visit, capturing the data and coordinating associated care management issues. No in-the-room intrusion and the provider can focus 100% of the patient. Now, that’s attractive … I am going to look deeper into this one.
athenahealth always has such a fun crew at their booth. Jonathan Bush was holding court (I got an short audience) in the central couch pit. It was just too much fun watching the procession of folks flowing in and out and the antics of the inimitable JB.
I’ve more, but my head has gone from throb to cannon fire…more HIMSS views tomorrow.
TUESDAY
Despite his humble protestations, Mr. H did a FANTASTIC job with the oratory when he, Inga, and Dr. Jayne made their first ever live-and-in-person show at the HIStalk sponsors’ lunch Tuesday and Maggiano’s. Inga’s boots were incredible and you could even see her just beaming, even through the surgical mask. They say they were Nervous Nellies, but they must cover well because it didn’t show. There was an absolutely incredible turnout with an amazing assortment of vendor bigwigs from all about the HIT world. A few glitches with food service aside, I think they did a knockout job. Mr. H and Inga even hand-wrote personal messages on thank you cards to each of the attendees and I overheard many comments on how nice or how funny the remarks were. All I can say is if you were invited and didn’t make it by, you missed out.
I had a sit-down with Dana Sellers of Encore. She is just as delightful to talk with as Ivo. I love their corporate philosophy and, especially, their slogan of “100% Referenceability.” Make your clients happy – all of them, all of the time. High standards, but their growth and abilities to attract and keep quality IT folks in the current market when those peeps are getting hard to find seems to add validity to their approach.
GE Centricity Advance is now shooting for docs in my neck of the woods (small practices). They seem to have learned some good stuff since I last looked at Centricity and their Mobile version, which is coming in Q2, appears to build even further upon those lessons. (Honestly, I never liked the look of Centricity, but the new Advance and Mobile stuff … much better.)
The trick shots on the pool table at the Iatric booth were very cool.
Ingenix says they’re now looking to thicken the relationships that have spread out so much in their recent buying frenzy. The buying may continue (as it will across the whole HIT market, eh?) but they want those thin ties to strengthen as they work to establish more “integrationability” (my word) across their many arms. Expect some rebranding soon. I like their stated open-to-sharing mindset.
Thomson Reuters has some really cool clinical decision support tools out or coming for physicians, pharmacies, infection control, pediatrics, and more which all benefit from the “same source of truth.” (I like that line.)
MEDHOST touchscreen tools and floor plans for EDs are not in my every day realm, but I really liked how they look and feel.
The Man & Machine waterproof keyboards and mice demo with waterfalls running over these tools was simple, slick, and effective. Contagion control is as, if not more, vital than data capture, I would wager to say.
Onyx and Stinger Medical had some really cool-looking carts and display tools for hospitals that just looked smart.
I felt like Maxwell Smart in the Unity Medical “cone of silence.” I want one.
Lastly, I noted how irritated I kept feeling as I tried to take in as much as I could in my limited window of time at HIMSS. Then, a quick calculation helped me realize it was a “setup for failure” kind of event. With somewhere around 1,000 vendors, if you only spent one minute with each, it’d still take over 16.6 hours to see all there was to see. And, that doesn’t even include the Interoperability Showcase, the education sessions, assorted keynotes, or bathroom breaks.
What a show.

E-mail Gregg.















































































































It's nice when Epic takes on patent trolls and other bad actors in the industry. They do great when they…