Healthcare AI News 4/10/24
News
Google opens Gemini 1.5 Pro to developer preview via API, which includes native speech understanding and a file handling API. The system was tested with a 400-page transcript from the Apollo 11 mission, about which it could answer questions and details from conversations and images using up to 1 million tokens.
Meta says it will release its Llama 3 open source LLM within one month, with double the parameter size of Version 2 and about the same as Open AI’s GPT-4.
Business
Bayer and Google Cloud will collaborate on developing AI solutions for radiologists.
Northwestern Medicine and Dell’s AI Innovation Lab create an LLM solution for drafting x-ray reports. They are also working on a predictive model for the EHR.
All of India’s major hospital chains are using AI, with Apollo Hospitals testing it for patient monitoring, cardiovascular disease prediction, symptom checking, radiology workflow, and in-room automation. Apollo says that some of the technologies have earned US FDA clearance.
Research
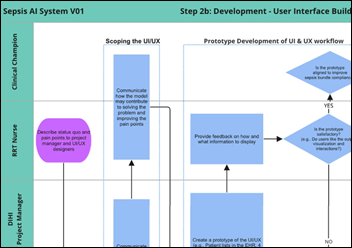
Researchers document the steps that were involved in Duke University Health System’s design, development, and maintenance of the AI-powered SepsisWatch system. They hope to illustrate the lessons that were learned in developing algorithms, involving stakeholders, and setting up an organizational structure.
Researchers find that an algorithm can predict hospital-acquired pressure injury with 74% accuracy, extending EHR-calculated Braden Scales into an early warning system that could save a 500-bed hospital up to 90,000 labor hours and $18 million in expense each year.
Other


Penn’s medical school names Marylyn Ritchie, PhD, former director of biomedical informatics, its first vice dean of AI and computing. University of Pennsylvania Health System also promotes former radiology chief Mitchell Schnall, MD, PhD to SVP of data and technology solutions, with a focus on AI.
International health leaders list four action areas that should be addressed to fully realize AI’s healthcare potential:
- Identify high-priority data elements that are needed for AI applications and ensure that availability of those elements is reliable.
- Test AI tools to ensure that they are safe and effective within specific patient populations and are free of bias.
- Standardize business processes so that data can be shared between institutions, such as connecting encounter data to outcomes, and explore privacy-preserving data sharing approaches.
- Advocate for paying for value (quality, safety, health, and costs) to align the financial incentives for using AI.
Contacts
Mr. H, Lorre, Jenn, Dr. Jayne.
Get HIStalk updates.
Send news or rumors.
Contact us.



Today's post contains the phoenixes rising from the ashes of the post COVID telehealth era. There's two things that destroy…